The influx of food delivery apps has been a boon to most of us, as now we can satiate our craving sitting right where we are. We’re even served a plethora of options such as vegan food, ethnic fare, meal-kits, fast food, home cooked meals, diet food, and more.
The opening of such a niche in the delivery realm has given entrepreneurs and startups yet another domain related to the ever green food industry to invest and earn handsomely.
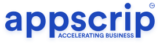
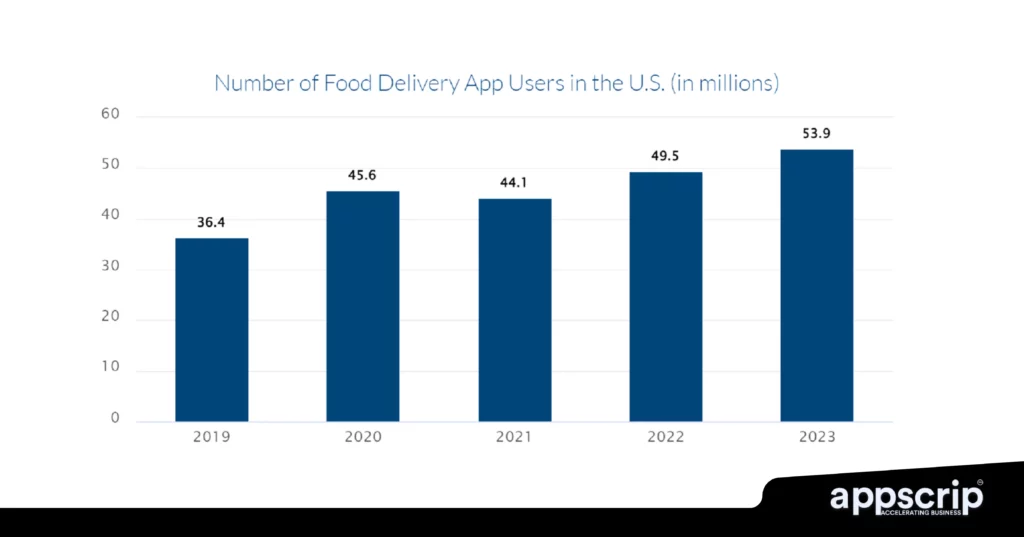
In 2025, the global online food delivery market is projected to hit $1.41 trillion, roaring at a CAGR of 7.88% through 2029. Let’s explore the top players in this sector and see what makes each of them stand out.
TL;DR
- Market Growth: By 2025 the global food delivery market is projected to reach $1.41 trillion, growing at 7.88% CAGR through 2029.
- Top Players: Uber Eats, DoorDash, and Grubhub dominate the landscape through extensive reach, innovative features, and friendly UI’s.
- Innovative Features: Smart recommendations, real-time tracking, subscription models, and loyalty programs enhance user experience.
- Emerging Technologies: AI, drone deliveries, cloud kitchens, and blockchain are transforming the industry.
- Benefits: Increased efficiency, personalization, and security make food delivery more accessible and reliable than ever before.
Top Food Delivery Apps
1. Uber Eats
- Inception & Overview: Uber Eats birthed in 2014 as a subsidiary of Uber Technologies, Inc. As on date their food delivery services are available across 6,000 cities in 45 countries.
- USP: Their global reach is unmatchable. And add this to fast and reliable delivery from your favourite local and chain restaurants.
- Revenue Model: Revenue is generated through delivery fees, service charges, and commissions from partner restaurants.
- Innovative Features: Smart recommendations powered by AI, based on past orders and user behaviour.
- Users can order in advance and collect their food without waiting.
How White-Label Solutions Can Help Regional Platforms Replicate Uber Eats’ Success:
Regional food delivery platforms can replicate Uber Eats’ success by adopting white-label solutions. These white label solutions like the one provided by Appscrip adopt pre-built technology enhancing time to market. These white-label platforms also offer customizable features adding value to the product.
- Example: A regional delivery app could use a white-label solution to integrate Uber Eats-like features (e.g., driver tracking, dynamic pricing, and customer support) without building them from scratch.
- Cost-Effective Scaling: White-label platforms reduce development time and costs, allowing regional players to scale operations rapidly.
- Local Adaptation: Unlike UberEats, which operates globally, regional platforms can use white-label solutions to cater to local food preferences, payment methods, and regulations, giving them a competitive edge in domestic markets.
· User Interaction Patterns
✅ Simple and clean UI – Users find ordering easy owing to the intuitive design and easy search functionality.
✅ Personalized recommendations – Using AI, the app suggests foods based on order history and preferences.
✅ Real-time tracking – Users use the live map feature extensively to track orders.
✅ Subscription model (Uber One) – Those who don’t cook often and prefer ordering, subscribe to save on delivery fees and earn discounts.
✅ Loyalty through rewards – Using the app regularly helps accumulate rewards and discounts.
🔸 Pain points: There are occasional delays, and high fees during peak hours.
- Revenue Generated:
- 2022: $10.9 billion
- 2023: $13.7 billion
- 2024: $15.2 billion
- Pros:
- Innumerable restaurant partnerships
- User-friendly interface
- Integration with Uber’s ride-sharing app
- Cons:
- Fees are on the higher side, when compared to the competition.
- Variable delivery times
2. DoorDash
- Inception & Overview: Originated in Palo Alto, California in 2013. DoorDash has gone on to become a leading food delivery service in the U.S., with presence in 4,000 cities.
- USP: Local businesses can increase their business due to the extensive coverage provided. DashPass subscription is a saving for regulars.
- Revenue Model: Earns through delivery fees, service fees, and commissions from restaurant partners.
- Innovative Features: DashPass subscription offers free deliveries and exclusive discounts.
- DoorDash Drive: Delivery service for businesses that don’t own a fleet.
· User Interaction Patterns
✅ “DashPass” subscription – Many users subscribe to DashPass for free delivery and discounted service fees.
✅ Group ordering – Users can create group orders and split payments.
✅ Customizable orders – Users to modify dishes and add notes for restaurants.
✅ Real-time driver communication – Users can chat with drivers to change or clarify delivery details.
🔸 Pain points: Errors in order fulfilment, limited restaurant options in smaller markets.
- Revenue Generated:
- 2022: $6.6 billion
- 2023: $8.0 billion
- 2024: $9.3 billion
- Pros:
- Wide restaurant options
- Subscription service (DashPass) for saving on fees
- Real-time order tracking
- Cons:
- Service fees can turn expensive
- Occasional delivery delays in peak times
3. Grubhub
- Inception & Overview: Established in 2004, Grubhub operates connecting diners with local restaurants in over 4,000 U.S. cities.
- USP: This food delivery pioneer offers flexible payment options and a loyalty rewards program.
- Revenue Model: Income is derived from delivery fees, service fees, and commissions charged to restaurants.
- Innovative Features: Grubhub+ loyalty program and other perks with cashback and special deals.
- Grubhub Sound Bites: Exclusive virtual concerts combined with food promotions.
· User Interaction Patterns
✅ Strong focus on discounts – Users love the regular discounts and promo codes that are a mainstay with Grubhub.
✅ Ease of reordering – Quick reordering past orders is a key feature.
✅ Order customization – Diners use the app’s order modification options regularly.
✅ Partnerships with restaurants –Grubhub has exclusive tie-ups with certain restaurants due to which many users are loyal to this app.
🔸 Pain points: UI is dated and there are issues with delivery times.
- Revenue Generated:
- 2022: $2.0 billion
- 2023: $2.3 billion
- 2024: $2.5 billion
- Pros:
- Well-established in the U.S.
- User-friendly platform
- Several payment options
- Cons:
- Stiff competition from other platforms
- Service fees can hurt at times
4. Postmates
- Inception & Overview: Founded in 2011 offers on-demand delivery from restaurants, grocery stores, and other retailers. In 2020, it was acquired by Uber, strengthening its market position in the U.S. food delivery sector.
- USP: Postmates with its stand out “delivers-anything” model — delivering not just food, but also groceries, alcohol, and retail items, making it a versatile delivery service.
- Revenue Model: Revenue generated through delivery fees, service fees, and merchant commissions.
- Innovative Features:
- “Delivers Anything” Model: Customers can order food, groceries, alcohol, and even retail goods from various merchants — a significant differentiation in the delivery market.
- Postmates Party: A feature offering free delivery on group orders from trending eateries, encouraging social ordering and larger basket sizes.
- Group Ordering: Users can invite others to contribute to a shared order, simplifying split payments and encouraging social engagement.
How Expanding into Multi-Category is a Growing Trend:
The success of Postmates’ multi-category delivery model reflects a broader industry shift toward consolidating food, grocery, and retail delivery under a single platform. Platforms looking to emulate this success can benefit from white-label and modular app development.
- Example: Appscrip offers modular app development that allows platforms to integrate multi-category offerings like groceries, alcohol, and retail products into a single app.
- Cost-Effective Scaling: Using a modular approach, platforms can launch new verticals without rebuilding their app architecture from scratch.
- Enhanced Customer Retention: Offering multiple categories within a single app increases customer engagement and order frequency — a key driver behind Postmates’ success.
· User Interaction Patterns
✅ Flexible Ordering Beyond Food – Users rely on Postmates as you can order groceries, alcohol, and convenience store items alongside food.
✅ Quick Delivery Option (“Postmates Unlimited”) – Free delivery on orders over a threshold, enhancing usage.
✅ Group Orders and Split Payments – Users can order together and split the payment.
✅ Scheduled Delivery and Customization – Schedule deliveries for events and even adjust orders.
🔸 Pain points: Inconsistency in delivery and the delivery fees can be high for small orders.
- Revenue Generated:
- 2022: $1.0 billion
- 2023: $1.2 billion
- 2024: $1.3 billion
- Pros:
- Delivers more than just food
- Quick delivery times
- Postmates Unlimited, subscription with reduced fees
- Cons:
- Limited availability
- Higher fees during rush hour
5. Deliveroo
- Inception & Overview: Founded in 2013 in London, Deliveroo operates in the UK, France, Belgium, Ireland, Italy, Singapore, the UAE, and Hong Kong. The platform connects users with local restaurants, offering food delivery services through a network of in-house couriers.
- USP: Focuses more on premium restaurant partnerships. Their delivery-only kitchens, known as “Editions,” help reach new areas without dine-in services.
- Revenue Model: Revenue through commissions charged to restaurants, delivery fees from customers, and subscription services like Deliveroo Plus, offering unlimited free delivery for a monthly fee.
- Innovative Features: Editions (Cloud Kitchens) with only deliveries and no dine-in facility.
- “Deliveroo Hop” for 10-minute grocery delivery using micro-fulfilment centers.
· User Interaction Patterns
✅ Wide Restaurant Network – Deliveroo provides access to both local restaurants and network chains.
✅ Subscription Model (“Deliveroo Plus”) – Users love free delivery and exclusive offers through subscription.
✅ Real-Time Tracking – Users rely heavily on real-time tracking to monitor deliveries.
✅ Exclusive Partnerships –Exclusive tie-ups with premium restaurants has HNI clientele.
🔸 Pain points: High delivery fees and limited availability in some regions.
- Revenue Generated:
- 2022: £2.03 billion
- 2023: £2.07 billion
- 2024: £2.07 billion
- Pros:
- Wide range of restaurant partnerships
- Innovative delivery-only kitchens
- Subscription service offering free delivery
- Cons:
- Self-employed couriers causes labour disputes
- High competition affects business
6. Just Eat Takeaway
- Inception & Overview: This was formed from the merger of London-based Just Eat and Amsterdam-based Takeaway.com in 2020.
- USP: Europe’s food delivery leader with an enviable list of local eateries and global brands.
- Revenue Model: Revenue through commissions charged to partner restaurants and delivery fees from customers.
- Innovative Features: AI-driven voice ordering and chatbot support
- Just Eat Pay: Corporate meal allowance program for employees
· User Interaction Patterns
✅ Wide Variety of Choices – Access to a broad range of cuisines from local restaurants to fast-food chains.
✅ Easy Reordering – Apps saves order history, enabling quick reorders.
✅ Contactless Delivery – Contactless delivery available, increasing user trust and safety.
✅ Delivery and Pickup Options – Users can opt for food delivery or pick it up themselves.
🔸 Pain points: Delivery gets delayed during peak hours and expensive service fees adds to frustration.
- Revenue Generated:
- 2022: €5.56 billion
- 2023: €5.90 billion
- 2024: €6.20 billion
- Pros:
- Strong brand recognition
- Extensive restaurant partnerships
- Cons:
- Challenges in achieving profitability
- Intense competition in the food sector
7. Wolt
- Inception & Overview: This Finnish tech company was founded in 2014, it specializes in food delivery and courier service.
- USP: User-friendly service, impeccable customer support and fast deliveries utilizing a network of couriers.
- Revenue Model: Revenue is derived from commissions charged to partners and delivery fees from customers.
- Innovative Features: Accurate ETAs at every delivery stage.
- Hyper-local delivery fleet ensures quick service in small cities as well.
· User Interaction Patterns
✅ User-Friendly Interface – Wolt’s easy and simple design helps users browse and place orders quickly.
✅ Curated Recommendations – Engagement rates are high as AI-based recommendations are highly personalized.
✅ Fast Delivery Times – Deliveries in 30 minutes enhances satisfaction.
✅ Multi-Category Orders – App delivers more than just food, including groceries and pharmacy items.
🔸 Pain points: Delivery fees are steep and limited availability outside major cities cuts overall visibility.
- Revenue Generated:
- 2022: €345 million
- 2023: €420 million
- 2024: €500 million
- Pros:
- User-friendly interface
- High customer satisfaction
- Cons:
- Limited presence outside Europe
- Operational challenges in scaling
8. iFood
- Inception & Overview: This Brazilian online food delivery service founded operates in Brazil and LATAM.
- USP: Known for its speed, affordability, and innovation.
- Revenue Model: Revenue from commissions charged to restaurants and delivery fees from customers.
- Innovative Features: Autonomous delivery plans in Brazil using drones and robots.
- AI-powered kitchens optimizing pre-delivery operations.
· User Interaction Patterns
✅ Market Dominance in Brazil – Strong presence in Brazil with 80% market share.
✅ Subscription Model (“iFood Plus”) – iFood plus offers free delivery and discount benefits.
✅ AI-Driven Personalization – Recommendation engine helps discover new dishes and restaurants.
✅ Payment Flexibility – Pay via credit cards, debit cards, wallets, or cash.
🔸 Pain points: Service reliability poor in smaller cities, and app crashes during high traffic.
- Revenue Generated:
- 2022: $900 million
- 2023: $1.1 billion
- 2024: $1.3 billion
- Pros:
- Market leader in Brazil
- Strong logistics network
- Cons:
- Limited international presence
- Dependence on the Brazilian market
9. Swiggy
- Inception & Overview: Founded in 2014, this Indian online food ordering and delivery platform operates in over 580 Indian cities.
- USP: India’s go-to food delivery app with reliable service and a wide restaurant network. It has also diversified into grocery delivery and other services.
- Revenue Model: Revenue is generated through commissions from restaurants, delivery fees from customers, and subscription services.
- Innovative Features: Swiggy Genie: On-demand courier service.
- Instamart: 30 minutes ultra-fast grocery and essentials delivery.
· User Interaction Patterns
✅ Hyperlocal Delivery Model – High order accuracy and speed by focussing on fast delivery from nearby restaurants
✅ Swiggy Genie and Instamart – Provision to order groceries, medicine, and even documents alongside food.
✅ Subscription Model (“Swiggy One”) – User retention through free deliveries and exclusive discounts.
✅ Live Order Tracking – Real-time order tracking improves transparency and user satisfaction.
🔸 Pain points: High service charges and minimum order value deter some users.
- Revenue Generated:
- 2022: ₹5,700 crore
- 2023: ₹8,000 crore
- 2024: ₹11,247 crore
- Pros:
- Extensive delivery network
- Diverse service offerings
- Cons:
- High competition with Zomato
- Challenges in achieving profitability
10. Menulog
- Inception & Overview: This Australian and New Zealand online food and beverage ordering app was founded in 2006.
- USP: Australia and New Zealand’s favourite service with no hidden fees. It partners with local restaurants offering a wide range of cuisines.
- Revenue Model: Revenue is generated through commissions and delivery fees.
- Innovative Features: Restaurant tracking for a personalized delivery experience.
- No service fees for local restaurants, supports small entities.
· User Interaction Patterns
✅ No Delivery Fee for Some Restaurants – No delivery fees attract a lot of users and encourages loyalty.
✅ Wide Restaurant Network – Diverse restaurant partnerships enhances choice.
✅ Pre-Order and Schedule Deliveries – Users can plan meals in advance.
✅ Flexible Payment Options – Multiple payment methods like credit card, debit card, online payments and digital wallets.
🔸 Pain points: Slow delivery times and inconsistent order accuracy.
- Pros:
- Extensive network of restaurant partners
- User-friendly platform
- Cons:
- Facing competition from other delivery services
- Dependence on local market dynamics
11. Delivery Hero
- Inception & Overview: Founded in 2011, this German multinational online food-delivery service operates in over 50 countries.
- USP: Focuses on both local delicacies and global brands in over 70 countries. It offers delivery and pick-up options.
- Revenue Model: Revenue is generated through commissions, delivery fees from customers, and additional services like advertising.
- Innovative Features: AI-powered food trend analysis helps optimize restaurant offerings.
- Dark stores enable ultra-fast grocery deliveries.
· User Interaction Patterns
✅ Global Presence – Operates in over 70 countries.
✅ Multi-Service Platform – Users engage with the app for food, groceries and other essentials.
✅ Fast Deliveries with Real-Time Tracking – Quick delivery times and live tracking.
✅ Promotions and Discounts – Region-specific deals and discounts keeps users guessing.
🔸 Pain points: High service fees and minimum-orders are pain points.
Profitability challenges in certain markets
- Revenue Generated:
- 2022: €8.6 billion
- 2023: €9.9 billion
- 2024: €10.2 billion
- Pros:
- Global presence with a diverse portfolio
- Strong technological infrastructure
- Cons:
- Operational complexities due to vast scale
- Profitability challenges in certain markets
Business Models and Monetization Strategies
To ensure sustainability and profitability food delivery apps generate revenue through various means. Some of the most effective monetization strategies are:
Commission-Based Model for Restaurants
This is the most common strategy that most food delivery platforms engage in. They take a cut or a a commission on each order placed through the app. This works in two ways:
- Fixed Commission Rate: A percentage (e.g., 15-30%) is charged on each order.
- Tiered Commission Structure: Premium visibility comes with higher fees and lower fees for smaller restaurants.
Subscription and Membership Plans
Subscription offers users exclusive benefits for a fixed monthly fee, such as:
- Free or discounted delivery fees
- Priority customer support
- Exclusive deals from partner restaurants
In-App Advertising and Sponsored Listings
Food delivery platforms provides restaurants the option to pay for higher visibility through:
- Featured Listings: Restaurants appear at the top of search results.
- Banner Ads: Display promotions within the app.
- Discount Campaigns: Restaurants pay for promotions that offer special discounts, increasing order frequency.
White-Label Food Delivery Solutions
Some companies license their food delivery technology to other businesses through white-label solutions. With this restaurants can:
- Launch their own branded delivery apps
- Get access a pre-built infrastructure without developing an app
- The platform provider’s revenue comes through setup fees and subscription charges.
Emerging Technologies Shaping the Future
As the food delivery industry moves on, new technologies are making inroads changing how businesses operate and customers order food.
The Role of AI and Machine Learning in Food Delivery
AI is revolutionizing and transforming the food delivery niche by enhancing efficiency and personalization. Key applications that AI has modernised are:
- Smart Order Predictions: AI helps restaurants manage inventory by predicting demand by studying ordering patterns.
- Chatbots for Customer Support: The biggest grouse of customers was wait time, which has been mitigated via automated chatbots that handle common queries.
- Dynamic Pricing Models: The ability to ‘up and down’ your prices as per demand has been made possible through AI intervention. Prices are adjusted based on demand, location, and peak hours.
- Fraud Detection: Fraud will always hurt us, but with machine learning algorithms we can identify suspicious transactions and cut the losses.
Drone and Robot-Based Deliveries
Last-mile food delivery is the last debacle to overcome. Now technologies that can make a difference include:
- Drones: For faster, contactless deliveries in urban and remote areas.
- Autonomous Delivery Robots: Self-driving bots will deliver food, cutting human labour.
- Smart Delivery Lockers: Customers can collect their orders from secure pickup stations.
Although regulatory challenges remain, this technology promises reduced delivery costs, faster fulfilment and customer satisfaction.
Cloud Kitchens and Virtual Restaurants
The rise of cloud kitchens (ghost kitchens) is changing the basics of food delivery. These are delivery-only restaurants that operate efficiently and handle huge loads ensuring profitability. Key benefits include:
- Lower Overheads: As these can be located in low cost regions.
- Multiple Brand Operations: A single kitchen can take care of the requirements of multiple brands.
- Faster Expansion: Restaurants can make their presence felt in newer markets with minimal investment.
Blockchain for Transparent Transactions
Blockchain technology is just right for security and transparency in food delivery as it can ensure:
- Payment Security: Fraud is reduced through decentralized transactions.
- Tracking Food Supply Chains: Customers can satisfy themselves by verifying the origin of certain ingredients.
- Smart Contracts for Payments: Automated transactions can be carried out between restaurants, delivery agents, and platforms.