SaaS is changing how businesses perceive, operate and utilise software. By 2030, the global SaaS market is expected to reach $908.21 billion, growing at 18.7% CAGR. SaaS lets organisations focus on its core competencies, while accessing innovative tools, enhancing efficiency, reducing costs, and driving success.
This pay-as-you-go software offers remote access for improved collaboration, while reducing IT burden and enhancing scalability. What comes along is automatic updates, quicker deployment, and better integration.
Businesses plotting – SaaS or Traditional Software – will firstly have to fathom the differences between the two to succeed in their digital evolution. While traditional software is renowned for control and security; SaaS has a plethora of advantages that has many takers.
Read on, our blog will provide a detailed comparison of the two models to help entrepreneurs and businesses take an informed decision based on one that would best suit their needs and growth strategies.
TL;DR: SaaS or Traditional Software
SaaS (Software-as-a-Service): Features of SaaS:Cloud-based, Subscription-based, Automatic updates, Scalable & flexible, Remote access.
Traditional Software: Features: On-premise, One-time purchase, Manual updates, More control, Limited accessibility.
Which One to Choose?
- Go for SaaS if you need scalability, remote access, and hassle-free maintenance.
- Choose Traditional Software if you need full data control and compliance with strict regulations.
What is SaaS?
The greatest advantage SaaS applications offer – access using any device that boasts of an internet connection because they work on a cloud-based software delivery model. Secondly, these are subscription-based. These applications are typically hosted and managed by a third-party provider like a payroll service provider.
Key characteristics of SaaS:
- Cloud-based delivery model – There’s no need for local installation as the software is hosted remotely.
- Subscription-based pricing – SaaS being subscription based, businesses save on a large upfront investment by paying a monthly or annual fee.
- Automatic updates and maintenance – The user need not worry regarding updates, security patches, and server maintenance, as the provider takes care of these functionalities.
- Scalability – Businesses can save on cost as they have the option to change plans (upgrade or downgrade) based on the circumstance. This also takes care of scalability.
- Accessibility – SaaS applications are ideal for remote work or for any kind of collaboration as it is accessible from anywhere.
Examples of SaaS Platforms
- Salesforce – Businesses manage customer relationships, sales, and analytics using this cloud-based CRM platform.
- Google Workspace – Gmail, Google Docs, Drive, and the rest, are part of the suite of productivity tools with flawless collaboration that most businesses or individuals need.
- Dropbox – Users can store, share, and collaborate files across devices with the help of this cloud storage solution.
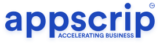
Early stage capital investments in various entities
What is Traditional Software?
This on-premise software is installed and operated on the user’s system or server. Traditional software is a one-time purchase (or licensing fee) with manual updates and maintenance.
The biggest benefit of traditional software is it does not rely on an internet connection to work. This provides better control but of course more resources are needed to manage operations.
Key characteristics of traditional software:
- On-premise installation – Traditional software is usually installed and operated on local servers (or individual systems).
- One-time purchase or licensing – In here you evade monthly or yearly subscription and make a one-time payment.
- Higher control over software and data – Industries dealing with strict compliance and security requirements prefer traditional software.
- Manual updates and maintenance – Goes without saying that the user is responsible for security patches, software updates, and system maintenance as the software is installed locally.
- Limited accessibility – Additional infrastructure is needed to access the software away from the premises. Access here is otherwise only on-site.
Examples of Traditional Software
- Microsoft Office (Pre-Cloud) – MS Office (Word, Excel, PowerPoint) was a locally installed software suite. Even QuickBooks, basic payroll systems, HRMS, CMS are designed for internal use.
- Adobe Creative Suite –Adobe software (like Photoshop and Illustrator) were standalone software and installed locally. But later transitioned to Adobe Creative Cloud.
SaaS vs Traditional Software: Key Differences
Businesses have their task cut out when they are out to choose between SaaS and traditional software. There are multiple factors to consider, as in cost, accessibility, maintenance, and customization.
Below is a detailed explanation of the key differences between the two models.
| Factor | SaaS (Software as a Service) | Traditional Software |
| Business Model | Subscription-based model with recurring monthly/annual payments. Costs are predictable, but could increase. Works on: Capital expenditure model (CapEx) | One-time licensing fee with periodic update costs. Higher upfront investment but no recurring fees. Works on: Operational expenditure model (OpEx) |
| Cost | Lower initial investment, making it ideal for startups. But, recurring payments could raise the total cost over time. | High upfront investment but no ongoingsubscription fees. Requires additional budgeting for maintenance and IT support. |
| Maintenance & Updates | Vendor handles updates, security patches, and server maintenance. Thus automatic access to the latest version is ensured. | Updates must be managed in-house, requiring IT teams. Compatibility issues may arise when upgrading. |
| Accessibility | Cloud-based, accessible from any device with an internet connection. Ideal for remote work and global teams. | Restricted to specific devices or networks where the software is installed, limiting flexibility. |
| Integration & Customization | Offers API integrations for easy connection with other tools. Provides pre-built customization options. | Custom development is often required for integration, which can be costly andtime-consuming. But the positive is better integrated customization. |
Advantages and Challenges
Every software model has its own pros and cons. This comparison will provide you with a clear understanding of both models. The next step would be to determine which model suits your operational needs, budget, and long-term strategy.
Advantages SaaS vs Traditional Software
| Advantage | SaaS | Traditional Software |
| Scalability | Easily scalable—businesses can upgrade or downgrade their plans based on needs. | Limited scalability—expanding requires purchasing additional licenses, hardware, and garnering IT support. |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Lower upfront costs—subscription-based model eliminates the need for expensive IT infrastructure. | High initial investment—requires a one-time purchase along with additional costs for IT infrastructure and maintenance. |
| Remote Accessibility | Cloud-based—accessible from any device with an internet connection, ideal for remote teams. | Access limited to installed devices or internal networks, restricting flexibility. |
| Automatic Updates & Maintenance | Vendor handles updates, security patches, and maintenance with no additional effort. | Updates and maintenance are managed in-house, requiring dedicated IT teams. |
| Integration & Customization | Supports seamless API integrations with other cloud applications. Pre-built customization options are available. | Allows deep customization but often requires costly and time-consuming development. |
Challenges SaaS vs Traditional Software
| Challenge | SaaS | Traditional Software |
| Data Security & Compliance | Data is stored on third-party servers, requiring businesses to trust vendor security measures. Compliance with regulations like GDPR or HIPAA can be complex. | Companies have full control over data storage, making compliance with strict regulations easier. |
| Internet Dependency | Requires a stable internet connection; downtime can impact business operations. | Functions offline without reliance on internet connectivity. |
| Long-Term Costs | Recurring subscription fees may result in higher total costs over time. | One-time licensing fee can be cost-effective in the long run but requires periodic investments in upgrades and maintenance. |
| Customization Complexity | Limited customization compared to traditional software—dependent on vendor’s features and API support. | Highly customizable but often requires in-house development expertise and additional costs. |
| Data Migration & Vendor Lock-in | Switching vendors or migrating data can be difficult and costly. | Once installed, businesses retain full ownership, but migrating to a new system is still a complex process. |
Latest Trends and Emerging Models
The software industry is a beehive of activity with constant innovation, businesses aiming to remain competitive and ahead of the race must be ready to imbibe emerging trends. Two key trends that are making waves on the future of software deployment are: integration of AI in SaaS platforms and the rise of hybrid models.
AI in SaaS Platforms
AI is transforming a majority of industries and it is also having a big say in SaaS platforms. AI is making SaaS platforms smarter, more efficient, and user-friendly. AI-powered SaaS solutions are on the purchase list of many organisations and in the process is rapidly gaining traction across domains.
Ecommerce has adopted AI-driven SaaS software, as many platforms now integrate with AI to personalise shopping experiences, optimize product recommendations, manage inventory, analyze customer behavior, and automate marketing efforts. All which are delivered through a cloud-based SaaS model.
The noteworthy positives that AI enables to SaaS are: the ability to enhance automation and improve user experiences.
Personalised User Experiences
- AI-driven SaaS platforms can customise services depending on user behaviour by utilising machine learning (ML) and predictive analytics.
- Personalised recommendations, intuitive dashboards, and efficient workflows enhance productivity and get operations flowing smoothly.
- Examples are AI-driven CRM systems that can gauge customer needs. While e-commerce platforms deploy dynamic pricing and product suggestions to enhance profit.
Enhanced Automation
- Repetitive tasks kill creativity, now thanks to AI in SaaS which enables automation of such tasks. Thereby reducing manual effort, improving efficiency and profitability in the long run.
- AI has a host of other features that have takers in many industries like automated customer support, AI-powered chatbots, and AI-garnered analytics that enhance user engagement.
- The greatest benefit that any organisation can profit from is faster decision-making, which is possible through AI-driven insights and workflow automation. This on the whole cuts down operational costs.
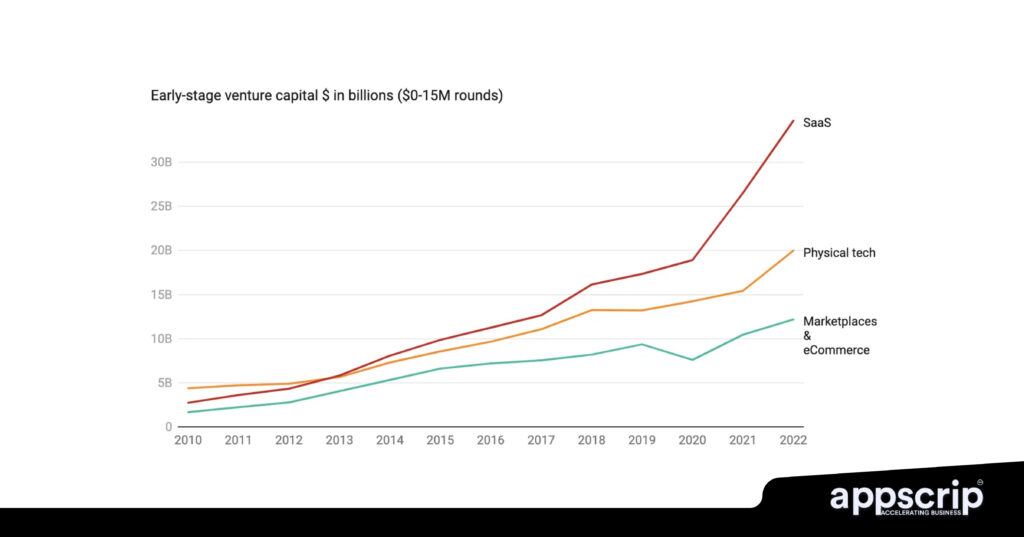
Successful SaaS companies in different countries
Hybrid Models
Even though there are obvious advantages of adopting SaaS – which many industries are doing. Some businesses feel the need to be able to combine the benefits of both models.
For example the qualities of traditional software that has been found wanting in SaaS are: compliance to regulations, data privacy assurance, and better customisation. This has given birth to hybrid models which combine both SaaS and traditional software whereby businesses can utilise the benefits of both models.
Combining SaaS and Traditional Software
- In hybrid models businesses can integrate traditional software with SaaS, thereby offering flexibility and security together – which are among the top features of both models.
- Therefore the strategy adopted by the organisations: instead of adopting SaaS totally, they use a combination of cloud and traditional software to balance cost, control, and compliance.
Use Cases and Industries Benefiting from Hybrid Models
- Healthcare and finance sectors are governed by strict data privacy regulations, but they are keen to imbibe the benefits accorded by SaaS. Hence these prefer hybrid models where sensitive data is kept on premise while analytics and automation benefits are sourced via SaaS.
- Even manufacturing and supply chain organisations employ a similar tactic to benefit from both models. While their ERP systems are on-premise they utilise SaaS for predictive analytics and logistics tracking.
- We also have many examples of large corporations using a hybrid model approach. They manage legacy software through IT strategies while SaaS is utilised for collaboration and productivity tools.
Is SaaS the Right Fit for Your Business?
Choosing between SaaS and traditional software is a huge responsibility and analyse carefully before deciding. Each business has unique needs which have to be taken into consideration before making a choice. Here’s the key factors to consider.
Key Considerations
Business Size and Growth Plans
- For Startups and small businesses that may be limited with capital during launch can certainly benefit from SaaS. SaaS is affordable and scales easily which makes it a good choice.
- But there are organisations with conditions to be met regarding the software they use. Especially larger enterprises, for such organisations a hybrid approach, balancing flexibility with control is a good idea.
- On certain occasions when you scale rapidly there may not be enough time to look at any other option other than SaaS. In such cases SaaS is a good option as it offers quick deployment and easy upgrades.
Industry Compliance Requirements
- In domains such as finance, healthcare, government, there are strict regulations to meet like GDPR, HIPAA, etc.
- There are SaaS providers who have built-in security and compliance certifications—but you would have to research the market and confirm it. IT management solutions can help businesses track and maintain compliance requirements effectively.
- If there’s a need for total control over sensitive consumer data with personal information that may be in the sights for cyber criminals, then traditional software may be the right option.
Budget and Resources
- SaaS is ideal for businesses with tight budgets as the initial investment is low.
- Traditional software has its benefits and is a one-time purchase. But remember it demands higher maintenance costs.
- And when you are doing financial planning or carrying out projections, then consider long-term expenses that incur in subscription fees vs. IT infrastructure costs.
Examples of Successful SaaS Adoption
Netflix: This entertainment channel with millions of subscribers on it moved from traditional data centres to a cloud-based SaaS model. With this approach Netflix has enabled global streaming scalability.
Shopify: Not all ecommerce platforms are big budgeted. Shopify helps SMBs to quickly set up stores and launch their services. This SaaS-based eCommerce platform makes sure small businesses can launch quickly without IT budgeting.
Slack: Workplace communication became vital especially during the pandemic period when people were forced to work remotely. Slack revolutionized workplace communication, out dating traditional messaging with a flexible, cloud-based system.
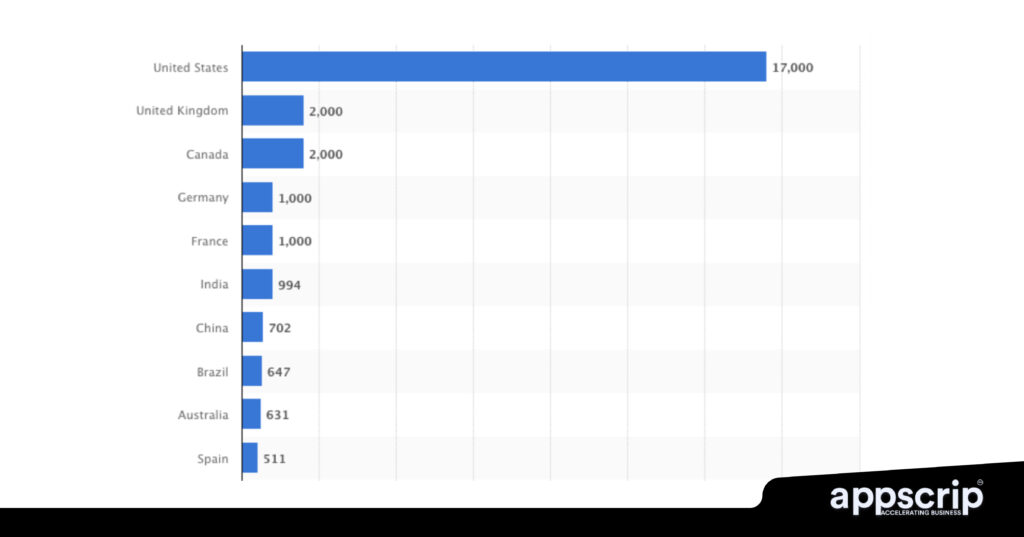
Top SaaS companies world over
Myths in SaaS vs Traditional Software
There’s a lot of misconstrued information about SaaS and traditional software. Let’s get the top myths that plague this scenario cleared for you.
Myth 1: SaaS is Only for Small Businesses
Truth: – False. SaaS companies fill most needs from document management to social media marketing, thus making them suitable for most domains. SaaS platforms cater to businesses of all sizes, including enterprises like Netflix, Shopify, Salesforce, Zoom, AWS, and Adobe Creative Cloud.
Myth 2: Traditional Software is More Secure
Truth: Not always. SaaS providers put in a lot of effort and invest heavily in security—often more than individual businesses can. They also take up activities such as regular updates, encryption, and compliance certifications to keep data safe.
Myth 3: SaaS is Always Cheaper
Truth: Not Really. SaaS is cheaper when you compare it to the upfront cost you save. But in the long run, that’s to be seen. This depends largely on your usage. In SaaS long-term usage subscription fees can add up. Traditional software may be cheaper in the long run for companies that don’t need frequent updates.
Myth 4: Switching from Traditional Software to SaaS is Too Hard
Truth: False. This is another myth that has a lot of takers. But it is not necessarily true. Many SaaS providers offer migration support, automated data transfer tools, and training programs to make the transition smooth.
How to Transition from Traditional Software to SaaS
Due to the benefits accorded by SaaS, many organisations are keen to migrate from traditional software to a SaaS solution. It has been proven that SaaS can significantly enhance operational efficiency, save costs and showcase business agility. However, to ensure a smooth and flawless transition with minimal disruption, a well-planned approach is key.
Key Steps for Transition
1. Evaluate Business Needs
- Businesses look for changes when they lack some functionality which is an absolute necessity. So, identify pain points and assess the limitations of your current software, which you know SaaS can address.
- Determine if SaaS would be the ideal option or a hybrid approach would be more suitable for your business.
- Also take into consideration key factors such as cost, scalability, security, and compliance to regulations.
2. Select the Right SaaS Platform
- The next stage would be to identify the various options you have. Check out different SaaS providers and their products. Compare features, pricing, offers, scalability, and integration capabilities.
- Give importance to smooth and flawless connectivity with existing systems. This can be ensured by preferring platforms that offer APIs and third-party integrations.
- Conduct a thorough research by checking out reviews, attend demos, and consult with industry experts before choosing a SaaS product.
3. Develop a Migration Plan
- Having a well-worked out migration plan is imperative to a successful implementation. A step-by-step migration plan needs to be worked out with necessary details such as data transfer, software integration, and testing.
- What is key here is to be aware of the timeline for each stage. With these estimates you would be able to reduce business disruptions and keep downtime to the minimum.
- A dedicated team needs to be selected and if necessary train them on how to go about the entire process. Assign the team to watch over the entire process – especially during the transition process and to be ready so attend to any issues or challenges.
Checklist for a Smooth Transition
Here’s how you can go about transitioning smoothly from your current software to SaaS. We have broken down the steps for easy understanding.
Data Migration Best Practices
- The main idea is not to lose any data. And for this you should backup the data before migration so as not to lose anything.
- Data cleansing techniques are also very much advised. This will help you to remove outdated or duplicate information that may be stored.
- After you have completed the data migration process it is a good idea to validate data integrity. This step will ensure accuracy of the data.
Training for Employees
- You have moved to the new platform to enhance operational efficiency. So ensure your staff are aware of how to use the software. Provide hands-on training and use mentoring software for ongoing guidance for them to adapt to the new platform.
- Additionally, consider incorporating a harvest forecast alternative to aid in resource planning and decision-making, which can further improve productivity and align operations with business objectives as your team becomes familiar with the new platform.
- Look for any user manuals, video tutorials, and customer support resources which your staff should be able to access in case of any need.
- The final step would be to take feedback. Encourage employees to provide feedback. This helps in two ways, one is you can be sure they’re using the software and secondly ensure they report any issues or glitches. These can be addressed without delay.
A well-planned migration is a key strategy to the transitioning to a SaaS set up. This ensures a smooth shift from traditional software to SaaS. On adopting SaaS, businesses can reduce IT overhead, enhance efficiency, and ensure they’re ready to scale in the future.
FAQs: SaaS vs Traditional Software
- What is the main difference between SaaS and traditional software?
Traditional software is a one-time purchase, but maintenance or support may incur additional costs. SaaS is subscription-based and cloud-hosted.
- What are the security implications of SaaS vs traditional software?
With SaaS, the responsibility for securing the application and infrastructure lies with the provider, but with traditional software, the user is responsible for managing security, and hence have more control over security measures but also need to actively manage them. SaaS relies on vendor-managed security.
- How can I decide whether SaaS or traditional software is better for my business?
Firstly clearly analyse your needs and your pain points. Even though costing plays a major role, that is not the only factor. Assess factors like scalability, integration needs, and compliance requirements.
- Can traditional software integrate with SaaS platforms?
Yes, it is possible. But the process requires specific tools and methods, which is again largely dependent on both entities. The integration is often achieved through APIs which allow the two systems to communicate and exchange data with each other.
Conclusion: SaaS vs Traditional Software
Both SaaS and traditional software have their own advantages and limitations. It’s up to the user, their preferences and on what they can compromise. The right choice depends on your business model, budget, and the needs of your niche.
SaaS offers advantages such as: access to latest software, scalability, remote capabilities, and lower upfront investment. While on-site or traditional software provides more control and is tailor-made for businesses that are governed by regulations, compliance clauses and strict security needs.
As businesses gain further awareness of the advantages of SaaS, the adoption of SaaS keeps growing. Appscrip provides SaaS development services for startups and entrepreneurs looking to adopt this technology so as to enhance their business processes.Want to know more? Get in touch.