In the past decade there has been a significant shift from traditional payments to digital payments. Payment gateways, the backbone of online transactions, are at the forefront of this change. These have evolved from basic transaction tools to advanced digital platforms.
From the rise of mobile payments to the integration of AI for security, new trends are reshaping how businesses and consumers interact.
In this blog we explore the future trends in payment gateways. We shall check out how these advancements are ensuring transactions get faster, safer, and more accessible, making the future of commerce safer.
Future Trends In Payment Gateways
Payment gateways are transforming at a quick pace because businesses and consumers are looking for more secure, efficient, and seamless ways to process transactions. New age technologies like AI, blockchain, and embedded finance are changing how payment systems operate, increasing convenience, security, and global reach.
Here’s a deep dive into the key trends shaping the future of payment gateways:
AI and Machine Learning in Fraud Detection
AI and machine learning (ML) are becoming the byword for identifying and preventing fraudulent activities in real-time. Usually it was the static rule-based systems that traditionally helped with detection of fraud.
But these systems could not keep up with the increasingly sophisticated fraud tactics that are in place today. Now AI and ML, enable dynamic, self-learning systems that adapt to new patterns of fraud and minimize loss.
How It Works:
- AI models have the capability to analyse large volumes of transaction data (payment patterns, device types, geolocation) to identify anomalies.
- Machine learning algorithms can detect suspicious activity, such as unusual spending behaviour or inconsistent IP addresses, and flag / block those transactions in real-time.
- AI also helps in customer authentication by analysing behavioural biometrics like typing speed, finger pressure and more.
Examples:
- PayPal: PayPal has an accuracy of 99% in identifying fraud by using AI to monitor over 500 million transactions every day.
- Stripe: Uses ML to identify between real and fraudulent transactions based on global transaction patterns.
- Adyen: Adyen uses AI-powered risk scoring to approve or decline payments instantly.
Impact:
- Reduced chargebacks and fraud-related losses.
- Improved customer trust and satisfaction due to fewer false declines.
- Faster transaction approvals, better user convenience.
Blockchain and Decentralized Payments
Future trends in payment gateways suggests Blockchain technology will cut out intermediaries and facilitate peer-to-peer (P2P) transactions. This is enabled by decentralized and secure payment processing. Blockchain transactions have greater transparency and security as they are verified by a distributed network of nodes.
How It Works:
- Payments are processed using self-executing agreements or smart contracts, wherein the terms are encoded directly into the blockchain.
- Cryptographic security ensures payment records cannot be changed and are resistant to hacking.
- Cross-border transactions are completed quickly and economically through decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms.
Examples:
- BitPay: A payment processor allowing businesses to accept Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies as payment.
- Coinbase Commerce: Enables merchants to accept payments in Bitcoin, Ethereum, and other cryptocurrencies without requiring a traditional bank.
- Ripple: Facilitates cross-border payments using its XRP token and blockchain network, enabling near-instant settlement.
Impact:
- Transaction costs are reduced by eliminating intermediaries.
- There’s higher transparency and security due to decentralized verification.
- International transactions happen quickly with real-time settlement.
Contactless and Biometric Payments
The adoption of contactless payments has been driven by the rise of mobile wallets and NFC (Near Field Communication) technology. Thus users can now make payments by just tapping their card or phone on the card reader or POS device.
Facial recognition and fingerprint scanning made possible due to biometric authentication also enhances the security and speed of these transactions.
How It Works:
- Secure communication is enabled between a device and a payment terminal to complete contactless payments using NFC or RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification) technology.
- A payment is approved using biometric authentication like Face ID or fingerprint scanning to verify the identity of the user.
- Data breaches are prevented by tokenization. Here sensitive payment data is converted into a unique token.
Examples:
- Apple Pay: Uses Face ID and fingerprint scanning to authorize contactless payments.
- Google Pay: Enables contactless payments through NFC and biometric authentication.
- Samsung Pay: Uses MST (Magnetic Secure Transmission) and NFC for contactless payments at most terminals.
Impact:
- User convenience and quicker checkout.
- Reliance on physical cash and cards reduces.
- Biometric verification and tokenization enhances security.
Embedded Payments and API-Driven Transactions
Users can complete transactions without leaving a platform with the help of embedded payments. Here payment processing capabilities are integrated directly into a product or service to complete transactions right from where they are.
Seamless communication between platforms and payment processors is made possible using APIs.
How It Works:
- APIs connect the payment processor with the UI, automating payment processing in the background.
- Features like one-click checkout and stored payment methods can be incorporated by businesses to customize the payment experience.
- Businesses can offer a branded payment experience using white-label payment gateways.
Examples:
- Uber: After a ride ends, payments can be processed in-app automatically.
- Shopify: One-click checkout can be offered by merchants by using embedded payment gateways (like Stripe).
- Amazon: One-click purchases are made possible by storing user payment details.
Impact:
- Smooth checkout process, increasing conversion rates.
- Businesses have greater control over providing a smooth payment experience.
- Faster and more secure transaction processing.
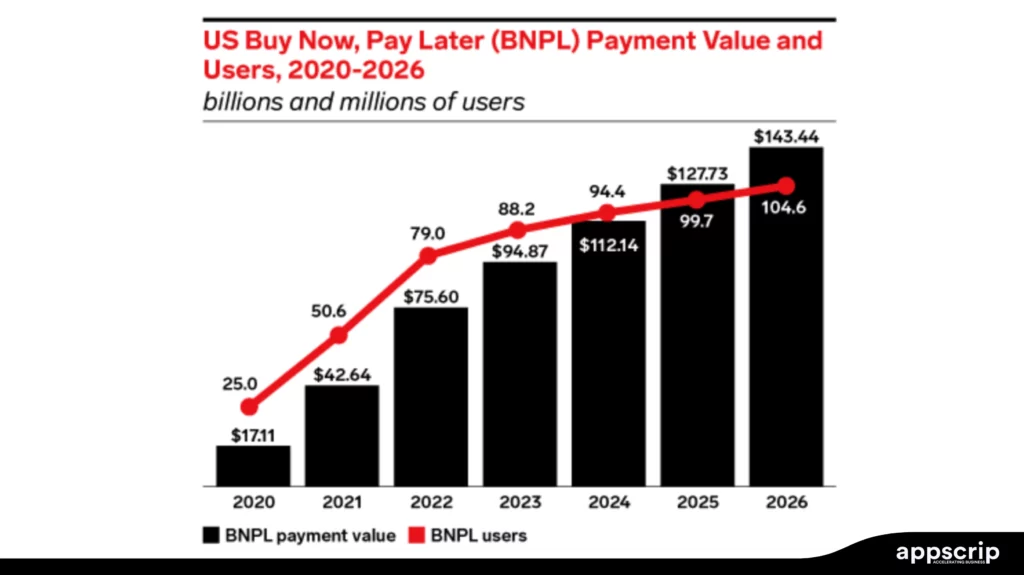
The Rise of Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) Culture
Future trends in payment gateways suggest BNPL will help customers to pay for the purchases they make in small interest-free instalments. This increases affordability and drives sales.
Payment gateways integrate BNPL options to cater to consumers interested in lessening the burden of making high value purchases and to enhance their purchasing power.
How It Works:
- Users select BNPL at the checkout as a payment option.
- The full purchase amount is recovered by the merchant upfront.
- The customer repays the amount in instalments (which could be interest-free) to the BNPL provider.
Examples:
- Klarna: Over 150+ million global users enjoy interest-free instalment payments.
- Afterpay: Users can complete the payments within six week by splitting it into four instalments.
- PayPal Pay Later: PayPal allows users to repay the principal over several months, this could be at a low rate of interest or even zero interest.
Impact:
- BNPL has seen to increase average order value (AOV).
- Higher customer conversion rates.
- Potential for greater customer debt and regulatory oversight.
Cross-Border and Multi-Currency Transactions
Global e-commerce has dissolved boundaries, helping sell wares on a worldwide scale. But then this has then brought about the need for payment gateways that support multiple currencies and real-time foreign exchange.
Payment gateways offer dynamic currency conversion and cross-border payment to enable international transactions.
How It Works:
- Payment gateways typically work by converting transactions in real-time into the local currency.
- FX (foreign exchange) rates are applied automatically.
- Localized payment methods like UPI in India and AliPay in China are included for better user acceptance.
Examples:
- PayPal: Supports over 200 countries and multiple currencies.
- Stripe: Offers real-time FX conversion and Stripe supports over 135 currencies.
- Adyen: Dynamic currency conversion helps processes international payments.
Impact:
- International buyers are not put on a limbo.
- Familiar local payment methods help increase sales.
- Operational costs can rise due to FX fees and regulatory requirements.
Security Challenges
In the digital payment ecosystem, payment gateways are vital components that facilitate transactions between merchants, customers, and financial institutions. But payment gateway systems are governed by several regulatory and security challenges.
We break them down for you:
The Impact of PSD2 and Open Banking
This EU regulation (PSD2 or the Revised Payment Services Directive) aims to transform the payments industry into a competitive field, make it innovative and secure.
It has impacted payment gateways by bringing in Open Banking. As per those guidelines, banks would have to use APIs to share customer data with third-party providers (TPPs).
Key Provisions of PSD2
- Strong Customer Authentication (SCA):
o Two-factor authentication (2FA) is imperative to complete online payments to mitigate fraud.
o As a result, the checkout process becomes complex because payment gateways must integrate SCA mechanisms.
- Access to Account (XS2A):
o As per this provision TPPs, that include payment gateways, are to be provided access to customer bank accounts (with their explicit consent) to either initiate payments or retrieve account information.
o This provision enhances innovation but makes it abundantly clear that payment gateways must comply with strict security standards.
- Regulatory Technical Standards (RTS):
o Technical requirements are specified for secure communication, authentication, and data protection.
Impact on Payment Gateways
- Increased Competition: Open Banking guidelines enables fintech startups and other entrants to offer payment services. Thus traditional gateways find themselves at loggerheads with them.
- Enhanced Security: Guidelines such as SCA reduce fraud. But in the process could cause an increase of abandonment rates if not carefully implemented.
- Operational Complexity: Investing in API integrations, compliance, and customer education becomes imperative for payment gateways.
- New Revenue Streams: Payment gateways can now in fact offer value-added services. With Open Banking data, payment gateways can provide financial analytics or personalized offers.
Challenges
- Implementation Costs: Any change or inculcating new technology or compliance to regulations require significant investment. The same is the case with adapting to PSD2.
- User Experience: Completing a sale is the key to the success of any enterprise. Hence balancing security (SCA) with a frictionless checkout experience will remain a key challenge.
- Data Security: Sharing data always gives room for cyberattack. The same is the case when data is transferred via APIs. The attack surface increases, and this necessitates robust cybersecurity measures.
Strengthening Cybersecurity Measures
Payment gateways are prime targets for cybercriminals due to the sensitive nature of the data they handle. To protect against fraud, unlawful activities, and data breaches enhancing cybersecurity is vital.
Key Cybersecurity Measures
1. Encryption:
o To protect data in transit and at rest it is vital to use advanced encryption standards (e.g., AES-256).
o The risk of exposure of sensitive data can be mitigated by tokenization, as tokenisation replaces sensitive data with unique tokens.
2. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA):
o One of the most prevalent methods of enhancing security is by adding another layer of security. This can be maintained by requiring users to verify their identity through multiple methods like SMS codes, biometrics.
3. Fraud Detection and Prevention:
o Machine learning algorithms analyse transaction patterns in real-time to detect suspicious actions and flag dubious activity.
o Potential threats are taken care of through real-time monitoring and alerts.
4. Secure APIs:
o APIs used for Open Banking and other integrations must be secured with OAuth 2.0, encryption, and rate limiting to prevent abuse.
5. Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing:
o To identify vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with standards like PCI DSS, conduct periodic checks and assessments.
6. Employee Training:
o Staff need to be educated on the basics of cybersecurity best practices to care against phishing attacks and insider threats.
Emerging Technologies
- Blockchain: Security is enhanced by providing a decentralized and immutable ledger for transactions.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Improves fraud detection and automates threat response.
- Zero Trust Architecture: Zero trust architecture assumes no user or device is trusted by default, but requires continuous verification.
Challenges
- Evolving Threat Landscape: Gateways need to stay ahead of cybercriminals with advanced defences. This is because cybercriminals are constantly trying to hack a system.
- Cost of Implementation: Maintaining high-quality cybersecurity measures can be expensive especially for smaller gateways.
- Balancing Security and Usability: There is a need to balance between stringent security measures and ease of completing transactions, as users can be frustrated by over-the-top security measures.
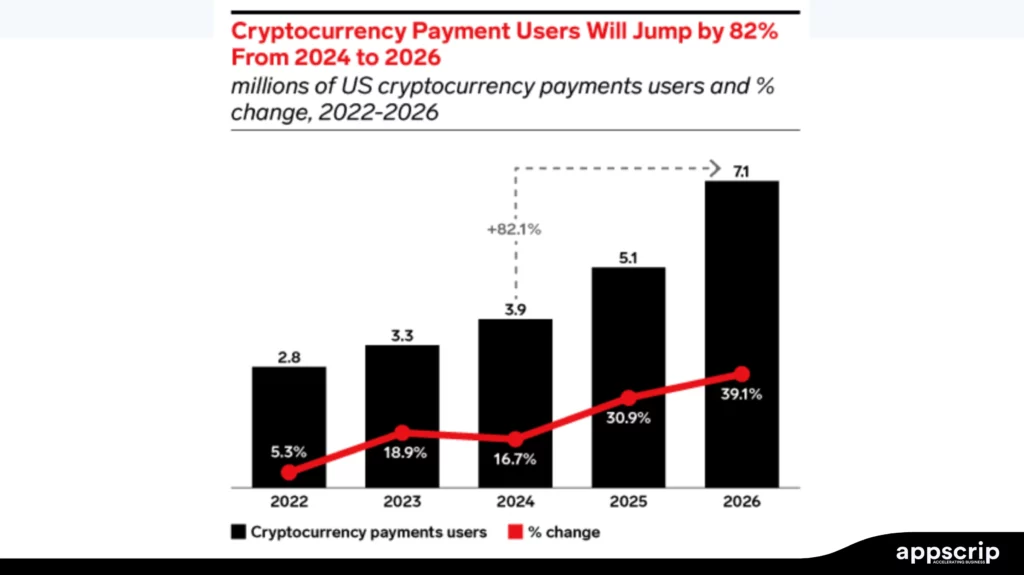
The Role of Cryptocurrencies and CBDCs in Payments
Online transactions are made possible using payment gateways. These are getting futuristic, thanks to their ability to handle cryptocurrencies and CBDCs. Such technologies are rewriting how money moves by learning how to handle Bitcoin’s wild swings to central banks’ vision to launch a digital currency.
Cryptocurrencies and CBDCs are payment gateway game-changers, while stablecoins easily transfer cash across borders. But CBDCs promise a leaner infrastructure, while crypto’s are a volatile lot. Revolut earning $5 billion in revenue for 2024 indicates what the future holds. But what we need is Hybrid gateways mixing CBDCs, stablecoins, and fiat.
Here’s the nitty-gritty on their roles, possibilities, and pitfalls.
Adoption of Stablecoins and Digital Currencies
Stablecoins Stealing the Show: Stablecoins like Tether (USDT) and USD Coin (USDC) are used for crypto payments and these are pegged to the dollar (e.g., $1 USDT = $1 USD). And these are any day better than Bitcoin’s fluctuating values. In 2024, stablecoin transaction volume hit $10 trillion by outplaying many traditional payment systems.
Digital Currencies on the Rise: Cryptocurrencies (Bitcoin, Ethereum) are not yet prevalent, but are certainly growing. Overstock and Tesla were among the first to accept them as fiat. But volatility keeps them at 2-3% of gateway use. CBDCs are still in their infancy with around 134 countries exploring them seriously.
Jamaica’s JAM-DEX, Nigeria’s eNaira, and the Bahamas’ Sand Dollar are live, with China’s e-CNY finding acceptance with 260 million wallets by 2023. The adoption of this system is slow, but is growing steadily. Around 5-10% of digital payments could be handled by CBDCs by 2030 if things go as planned.
Why It’s Happening: The main reason for the adoption of such tech is Speed (seconds vs. days), cost (pennies vs. dollars), and inclusion (1.4 billion unbanked get an account) drive this. Revolut’s forex success (£491 million in 2023) mirrors stablecoins’ appeal—fast, cheap, global. But it’s not that smooth—crypto’s uneasy acceptance by businesses and CBDCs’ regulatory lag keep them from growing.
How CBDCs Could Change Payment Infrastructure
Streamlined Systems: CBDCs could make gateways prevalent by cutting out middlemen. Today’s card networks like Visa, Mastercard charge around 2-3%. But a CBDC on a blockchain could settle instantly at near-zero cost, like Revolut’s interbank forex but backed by governments.
The BIS’s Project mBridge (China, UAE, HK, Thailand, etc.) tested in 2024, slashed cross-border settlement from 3 days to 10 seconds.
Two-Tier Twist: Most CBDCs (e.g., e-CNY, JAM-DEX, eNaira) use a “wholesale-retail” split. Firstly the central banks issue to banks, who then push it to wallets. This keeps gateways relevant but upgrades them.
For example Revolut distributing UK CBDC, blending its app’s ease with central bank trust. Retail CBDCs might even let you pay directly from a Fed wallet, sidelining PayPal entirely.
Big Shifts: Cash is slowly losing out, Europe has cut down usage of cash by 33% since 2014, as per McKinsey. Soon gateways might take up the CBDC route. Like Revolut’s $605 million card revenue shifting to digital sterling.
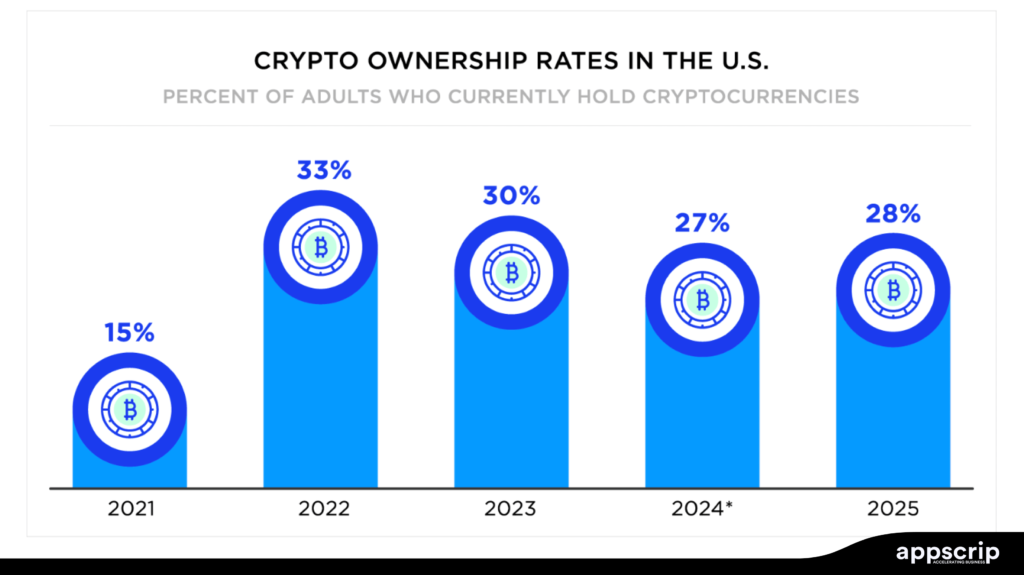
The Challenges of Cryptocurrency Payment Gateways
Volatility Vibes: Bitcoin is valued $80K one day and $90K the next. This would freak out even the sturdiest of the merchants. Gateways like BitPay convert to fiat instantly, but that’s not large scale.
Stablecoins help, but even Tether’s had troubles like 2% devaluation risk. Revolut overcomes this debacle by offering crypto as an option, it may not really be a smart idea but it limits loss.
Regulatory Rollercoaster: Due to Crypto’s wild nature, countries are circumspect, India bans it, the US taxes it, the EU’s MiCA (2024) tries to tame it. Gateways must KYC/AML every transaction and fines for slip-ups can have a huge impact, like how Coinbase was fined $50 million in 2023.
CBDCs don’t really find this a debacle as they have the backing of governments. But the real losers here are crypto gateways.
Tech Tantrums: Blockchain’s fast (Ethereum transacts at 15/sec), but not Visa-fast, which is really hot at 24K/sec. Scaling certainly isn’t for everyone, Solana found it the hard way at 65K tx/sec which caused the crash in 2024. But what hurts is the fees spike ($5-$20) when networks are busy.
In summary, while centralized platforms like Revolut offer enhanced security through controlled infrastructure, pure crypto gateways face significant challenges maintaining security and uptime due to their decentralized nature.
Case Studies
Stripe: AI-Powered Fraud Detection
Stripe has developed an advanced fraud prevention system called Stripe Radar, using ML to analyse billions of transactions across its network. Radar’s AI model continuously adapts by learning from historical fraud data and detects anomalies in real-time. Key features include:
- Risk-Based Authentication – Identifies high-risk transactions and puts additional security layers, such as 3D Secure.
- Adaptive Machine Learning – Constantly refines fraud detection models based on emerging threats.
- Customizable Rules – Merchants can set their own fraud detection rules to match business-specific needs.
Impact on Reducing Chargebacks and Improving Transaction Approval Rates
- Lower Chargeback Rates – Stripe Radar reduces fraudulent disputes by 25-40%, helping businesses save money.
- Higher Authorization Rates – By distinguishing between legitimate and fraudulent transactions, Stripe improves conversion rates, ensuring more successful payments.
- Seamless User Experience – Unlike traditional fraud detection systems that may block genuine transactions, Radar minimizes false narratives, allowing legitimate customers to complete purchases smoothly.
Shopify: Embedded Payments via API
Shopify Payments is an embedded payment solution that eliminates the need for third-party processors like PayPal or external payment gateways. By integrating payments directly within the Shopify ecosystem, merchants can:
- Accept multiple payment methods, including credit/debit cards, digital wallets (Apple Pay, Google Pay), and BNPL (Shop Pay Instalments).
- Automate tax calculations, refunds, and chargeback handling seamlessly.
- Avoid transaction fees associated with third-party payment providers.
API-Driven Transactions is Enhancing User Experience and Reducing Dependency on Third-Party Processors
- Frictionless Checkout – Shopify’s API ensures faster transactions by reducing payment redirections, leading to higher conversion rates.
- Scalability – Businesses can expand internationally with support for multiple currencies and local payment options.
- Security & Compliance – Shopify Payments is PCI-compliant and includes built-in fraud detection tools, reducing risks for merchants.